Dugongs
The Dugong (Dugong dugon) is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest modern relative, Steller's sea cow (Hydrodamalis gigas), was hunted to extinction in the 18th century.
The dugong is the only sirenian in its range, which spans the waters of some 40 countries and territories throughout the Indo-West Pacific. The dugong is largely dependent on seagrass communities for subsistence and is thus restricted to the coastal habitats which support seagrass meadows, with the largest dugong concentrations typically occurring in wide, shallow, protected areas such as bays, mangrove channels, the waters of large inshore islands and inter-reefal waters. The northern waters of Australia between Shark Bay and Moreton Bay are believed to be the dugong's contemporary stronghold.
Like all modern sirenians, the dugong has a fusiform body with no dorsal fin or hind limbs. The forelimbs or flippers are paddle-like. The dugong is easily distinguished from the manatees by its fluked, dolphin-like tail, but also possesses a unique skull and teeth. Its snout is sharply downturned, an adaptation for feeding in benthic seagrass communities. The molar teeth are simple and peg-like, unlike the more elaborate molar dentition of manatees.
The dugong has been hunted for thousands of years for its meat and oil. Traditional hunting still has great cultural significance in several countries in its modern range, particularly northern Australia and the Pacific Islands. The dugong's current distribution is fragmented, and many populations are believed to be close to extinction. The IUCN lists the dugong as a species vulnerable to extinction, while the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species limits or bans the trade of derived products. Despite being legally protected in many countries, the main causes of population decline remain anthropogenic and include fishing-related fatalities, habitat degradation and hunting. With its long lifespan of 70 years or more, and slow rate of reproduction, the dugong is especially vulnerable to extinction.
Dugong swimming in Libong Thailand
Dugongs are part of the Sirenia order of placental mammals which comprises modern "sea cows" (manatees as well as dugongs) and their extinct relatives. Sirenia are the only extant herbivorous marine mammals and the only group of herbivorous mammals to have become completely aquatic. Sirenians are thought to have a 50-million-year-old fossil record (early Eocene-recent). They attained modest diversity during the Oligocene and Miocene, but subsequently declined as a result of climatic cooling, oceanographic changes, and human interference.
Dugong dugon is the only extant species of the family Dugongidae, and one of only four extant species of the Sirenia order, the others forming the manatee family. It was first classified by Müller in 1776 as Trichechus dugon, a member of the manatee genus previously defined by Linnaeus. It was later assigned as the type species of Dugong by Lacépède and further classified within its own family by Gray and subfamily by Simpson.
Dugongs and other sirenians are not closely related to other marine mammals, being more related to elephants. Dugongs and elephants share a monophyletic group with hyraxes and the aardvark, one of the earliest offshoots of eutherians. The fossil record shows sirenians appearing in the Eocene, where they most likely lived in the Tethys Ocean. The two extant families of sirenians are thought to have diverged in the mid-Eocene, after which the dugongs and their closest relative, the Steller's sea cow, split off from a common ancestor in the Miocene. The Steller's sea cow became extinct in the 18th century. No fossils exist of other members of the Dugongidae.
Herd of Dugong grazing on eel grass on Libong Island Thailand (not my image)
Molecular studies have been made on dugong populations using mitochondrial DNA. The results have suggested that the population of Southeast Asia is distinct from the others. Australia has two distinct maternal lineages, one of which also contains the dugongs from Africa and Arabia. Limited genetic mixing has taken place between those in Southeast Asia and those in Australia, mostly around Timor. One of the lineages stretches all the way from Moreton Bay to Western Australia, while the other only stretches from Moreton Bay to the Northern Territory. There is not yet sufficient genetic data to make clear boundaries between distinct groups.
The dugong's body is large with a cylindrical shape that tapers at both ends. It has thick, smooth skin that is a pale cream colour at birth, but darkens dorsally and laterally to brownish-to-dark-grey with age. The colour of a dugong can change due to the growth of algae on the skin. The body is sparsely covered in short hair, a common feature among sirenians which may allow for tactile interpretation of their environment. These hairs are most developed around the mouth, which has a large horseshoe-shaped upper lip forming a highly mobile muzzle.This muscular upper lip aids the dugong in foraging. Bones in the forelimb can fuse variously with age.
The dugong's tail flukes and flippers are similar to those of dolphins. These flukes are raised up and down in long strokes to move the animal forward, and can be twisted to turn. The forelimbs are paddle-like flippers which aid in turning and slowing. The dugong lacks nails on its flippers, which are only 15% of a dugong's body length. The tail has deep notches.
A dugong's brain weighs a maximum of 300 g (11 oz), about 0.1% of the animal's body weight. With very small eyes, dugongs have limited vision, but acute hearing within narrow sound thresholds. Their ears, which lack pinnae, are located on the sides of their head. The nostrils are located on top of the head and can be closed using valves. Dugongs have two teats, one located behind each flipper. There are few differences between sexes; the body structures are almost the same. A male's testes are not externally located, and the main difference between males and females is the location of the genital aperture in relation to the umbilicus and the anus. The lungs in a dugong are very long, extending almost as far as the kidneys, which are also highly elongated in order to cope with the saltwater environment. If the dugong is wounded, its blood will clot rapidly.
The skull of a dugong is unique. The skull is enlarged with sharply down-turned premaxilla, which are stronger in males. The spine has between 57 and 60 vertebrae. Unlike in manatees, the dugong's teeth do not continually grow back via horizontal tooth replacement. The dugong has two incisors (tusks) which emerge in males during puberty. The female's tusks continue to grow without emerging during puberty, sometimes erupting later in life after reaching the base of the premaxilla. The number of growth layer groups in a tusk indicates the age of a dugong, and the cheekteeth move forward with age. The full dental formula of dugongs is 2.0.3.33.1.3.3, meaning they have two incisors, three premolars, and three molars on each side of their upper jaw, and three incisors, one canine, three premolars, and three molars on each side of their lower jaw. Like other sirenians, the dugong experiences pachyostosis, a condition in which the ribs and other long bones are unusually solid and contain little or no marrow. These heavy bones, which are among the densest in the animal kingdom, may act as a ballast to help keep sirenians suspended slightly below the water's surface.
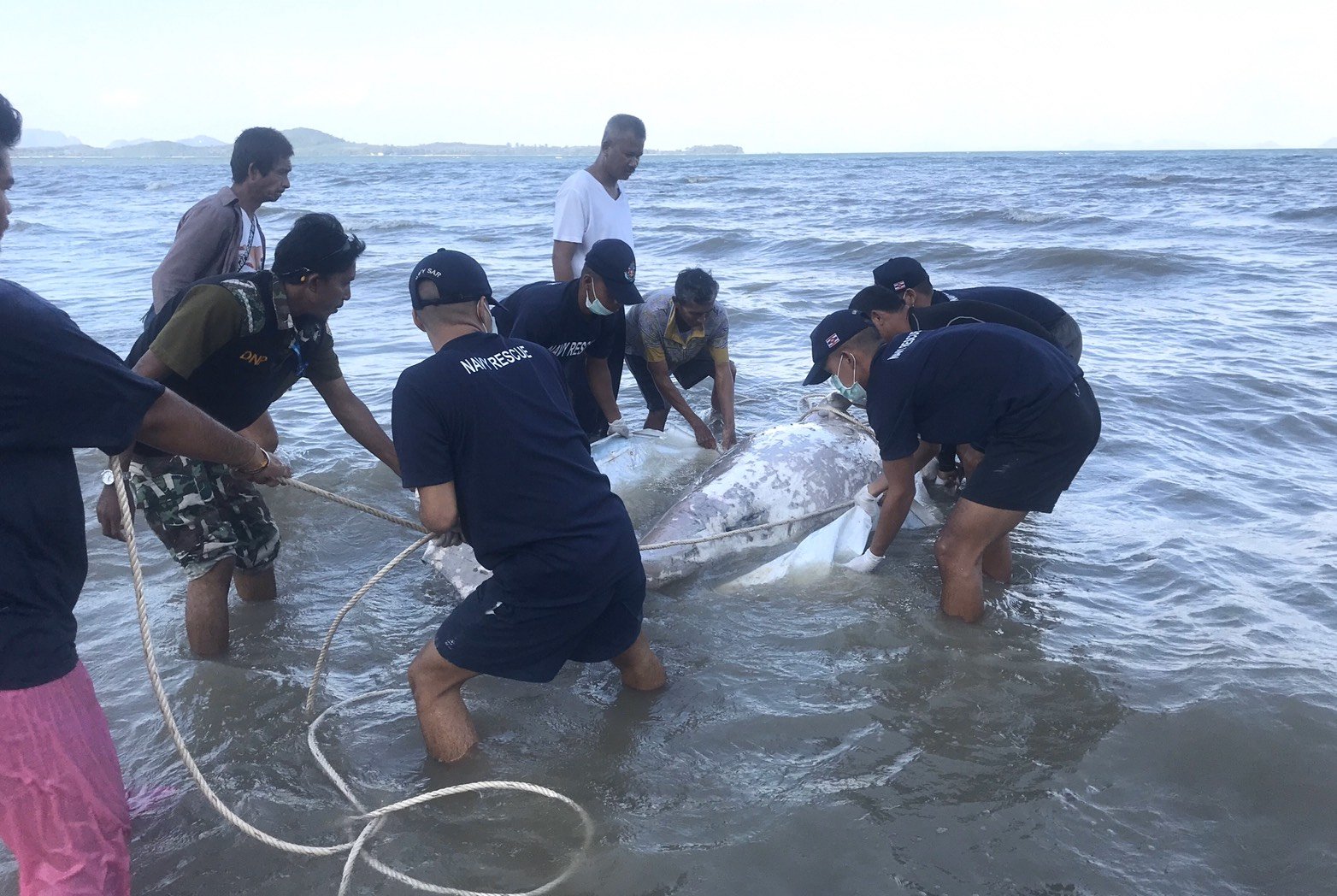
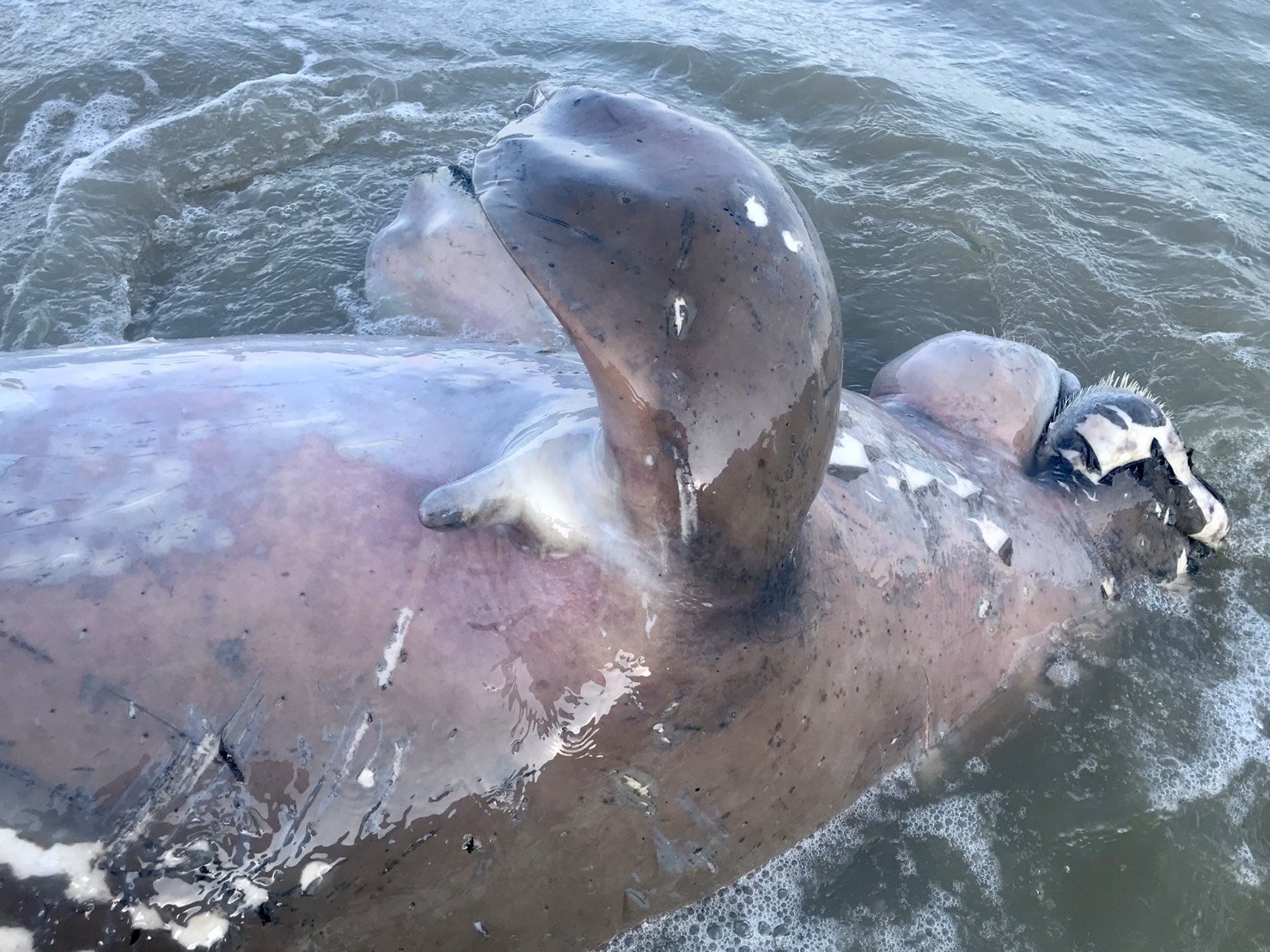
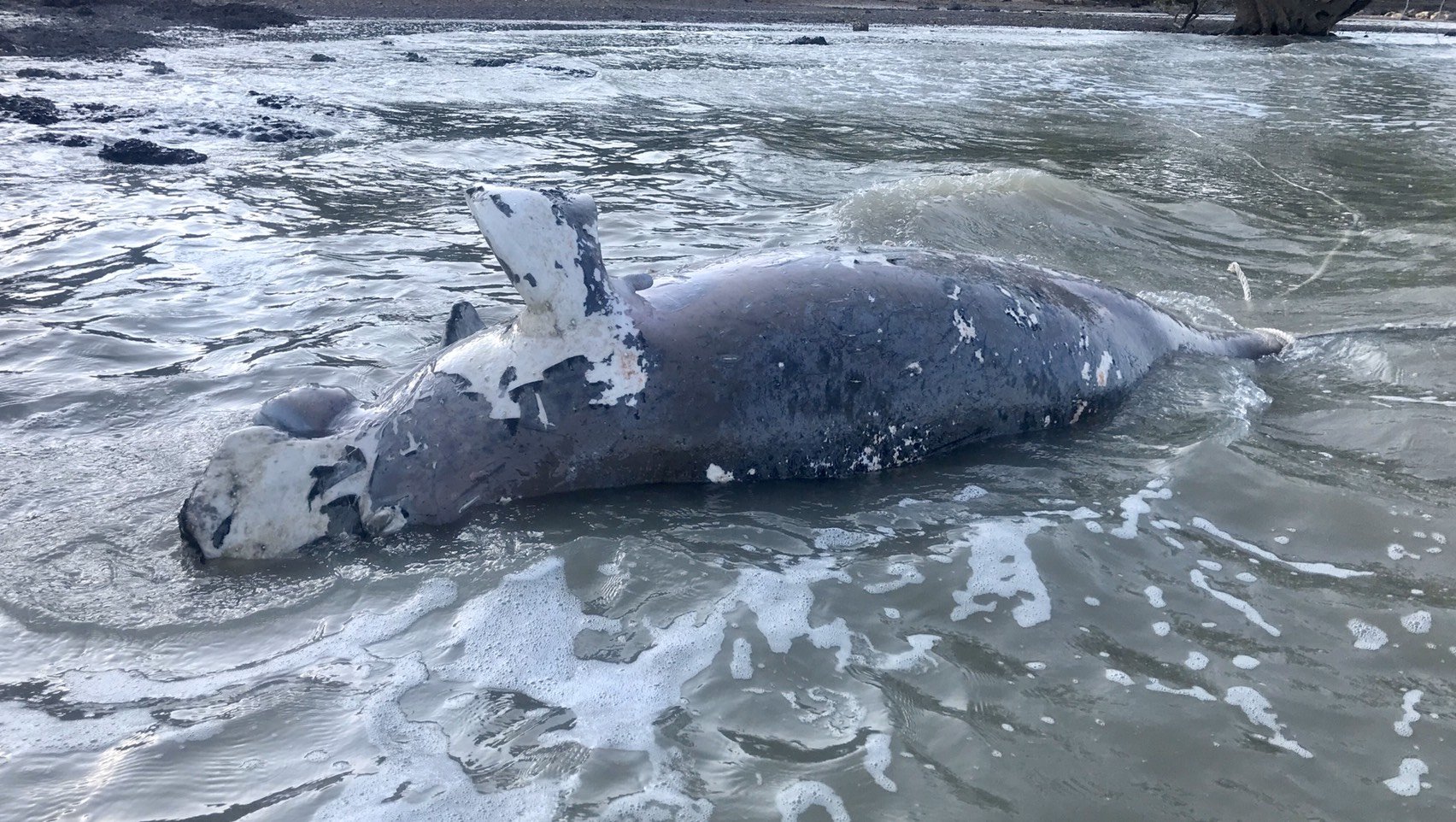
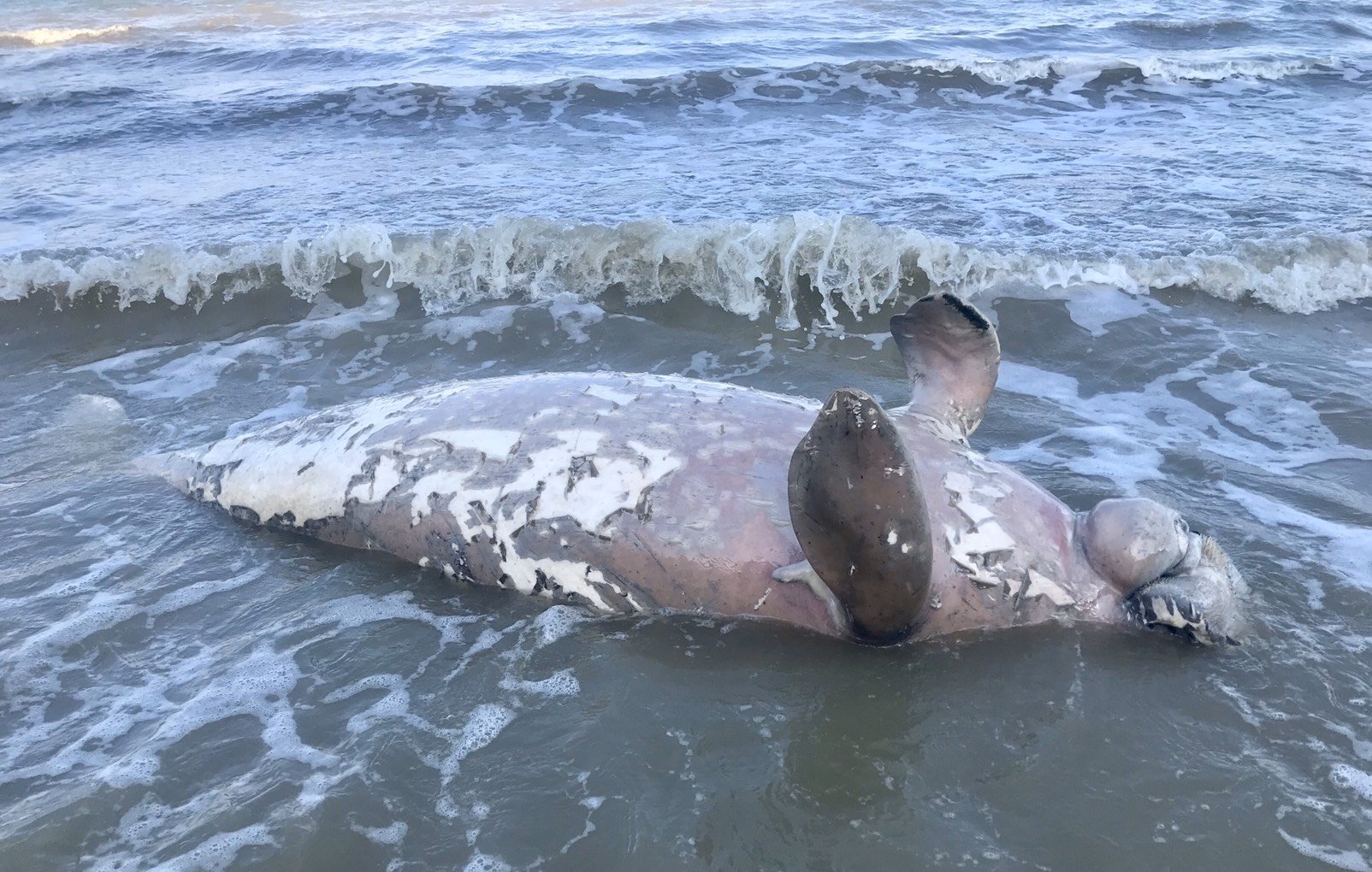
Deceased Dugong bull on my beach in front of my home in Koh Lanta, Krabi
An adult's length rarely exceeds 3 metres (10 ft). An individual this long is expected to weigh around 420 kilograms (930 lb). Weight in adults is typically more than 250 kilograms (550 lb) and less than 900 kilograms (1,980 lb). The largest individual recorded was 4.06 metres (13 ft 4 in) long and weighed 1,016 kilograms (2,240 lb), and was found off the Saurashtra coast of west India.[30] Females tend to be larger than males.
Dugongs are found in warm coastal waters from the western Pacific Ocean to the eastern coast of Africa, along an estimated 140,000 kilometres (87,000 mi) of coastline between 26° and 27° to the north and south of the equator. Their historic range is believed to correspond to that of seagrasses from the Potamogetonaceae and Hydrocharitaceae families. The full size of the former range is unknown, although it is believed that the current populations represent the historical limits of the range, which is highly fractured. Their distributions during warmer periods of Holocene might have been broader than today.[32] Today populations of dugongs are found in the waters of 37 countries and territories. Recorded numbers of dugongs are generally believed to be lower than actual numbers, due to a lack of accurate surveys. Despite this, the dugong population is thought to be shrinking, with a worldwide decline of 20 percent in the last 90 years. They have disappeared from the waters of Hong Kong, Mauritius, and Taiwan, as well as parts of Cambodia, Japan, the Philippines and Vietnam. Further disappearances are likely.
Dugongs are generally found in warm waters around the coast with large numbers concentrated in wide and shallow protected bays. The dugong is the only strictly marine herbivorous mammal, as all species of manatee utilise fresh water to some degree. Nonetheless, they can tolerate the brackish waters found in coastal wetlands, and large numbers are also found in wide and shallow mangrove channels and around leeward sides of large inshore islands, where seagrass beds are common. They are usually located at a depth of around 10 m (33 ft), although in areas where the continental shelf remains shallow dugongs have been known to travel more than ten kilometres (6 mi) from the shore, descending to as far as 37 metres (121 ft), where deepwater seagrasses such as Halophila spinulosa are found. Special habitats are used for different activities. It has been observed that shallow waters are used as sites for calving, minimizing the risk of predation. Deep waters may provide a thermal refuge from cooler waters closer to the shore during winter.
The images that follow are of an individual in Libong Island, Trang Province Thailand:

























































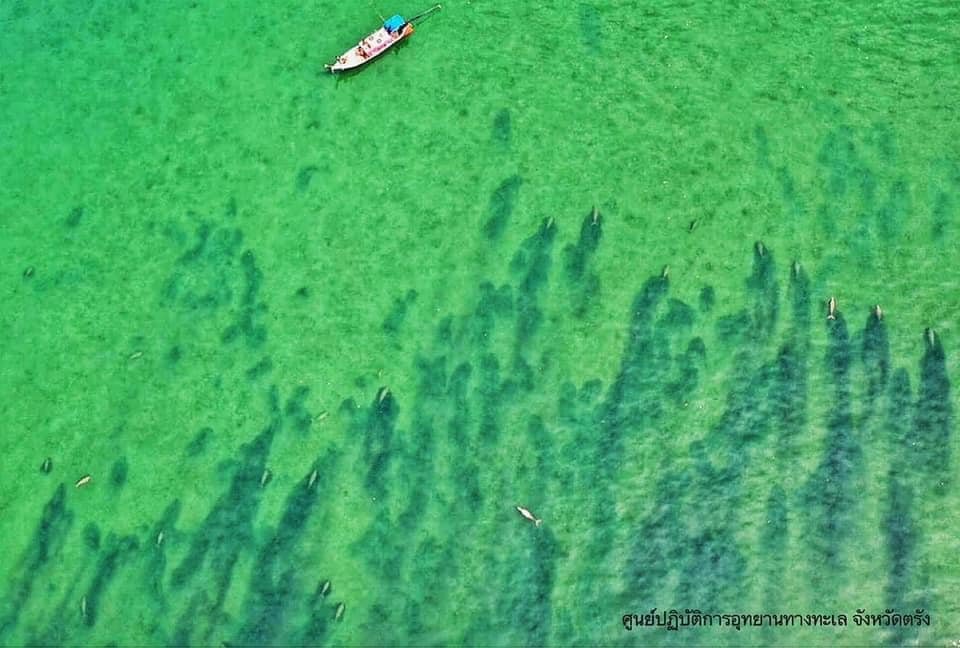
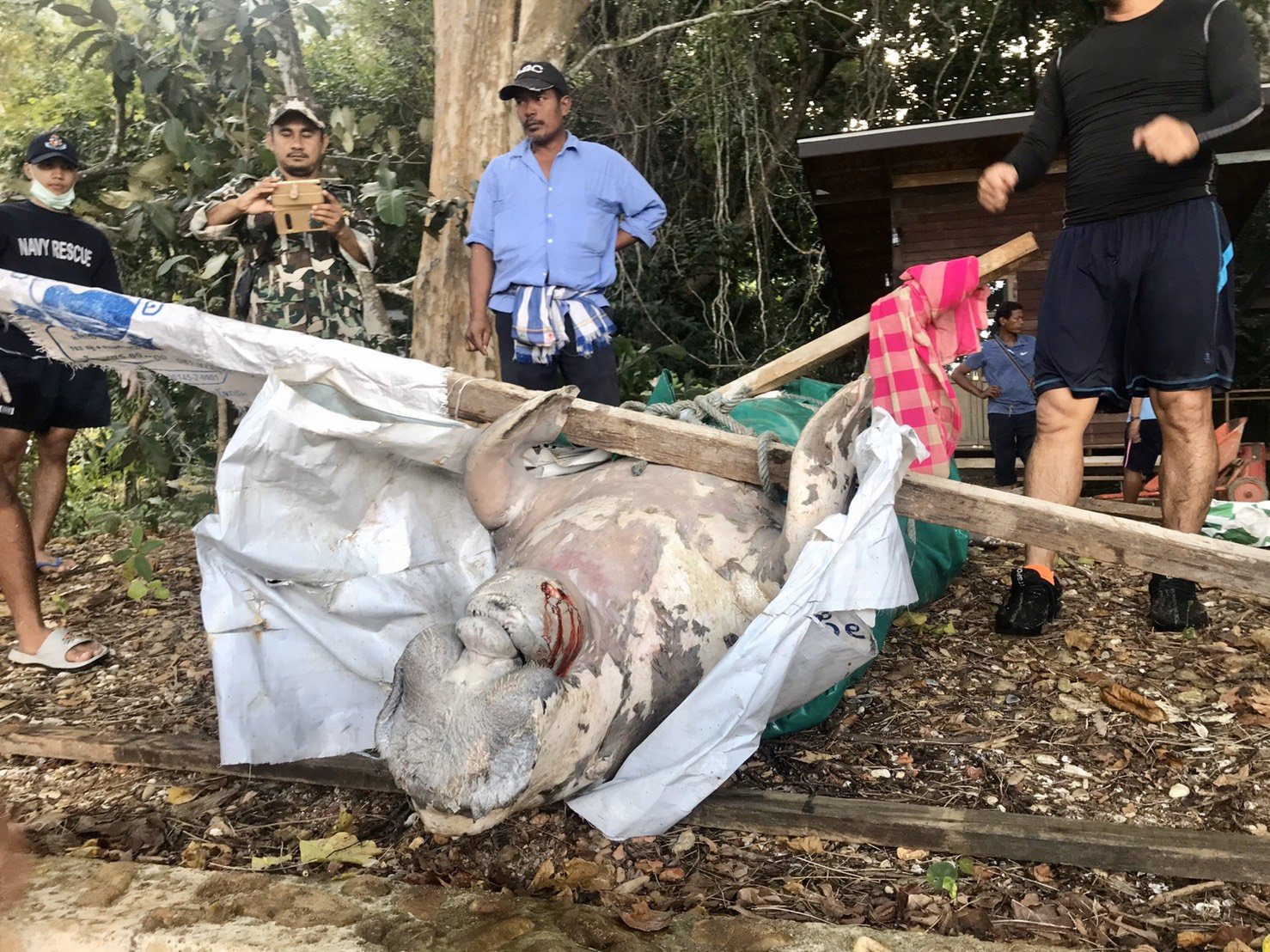
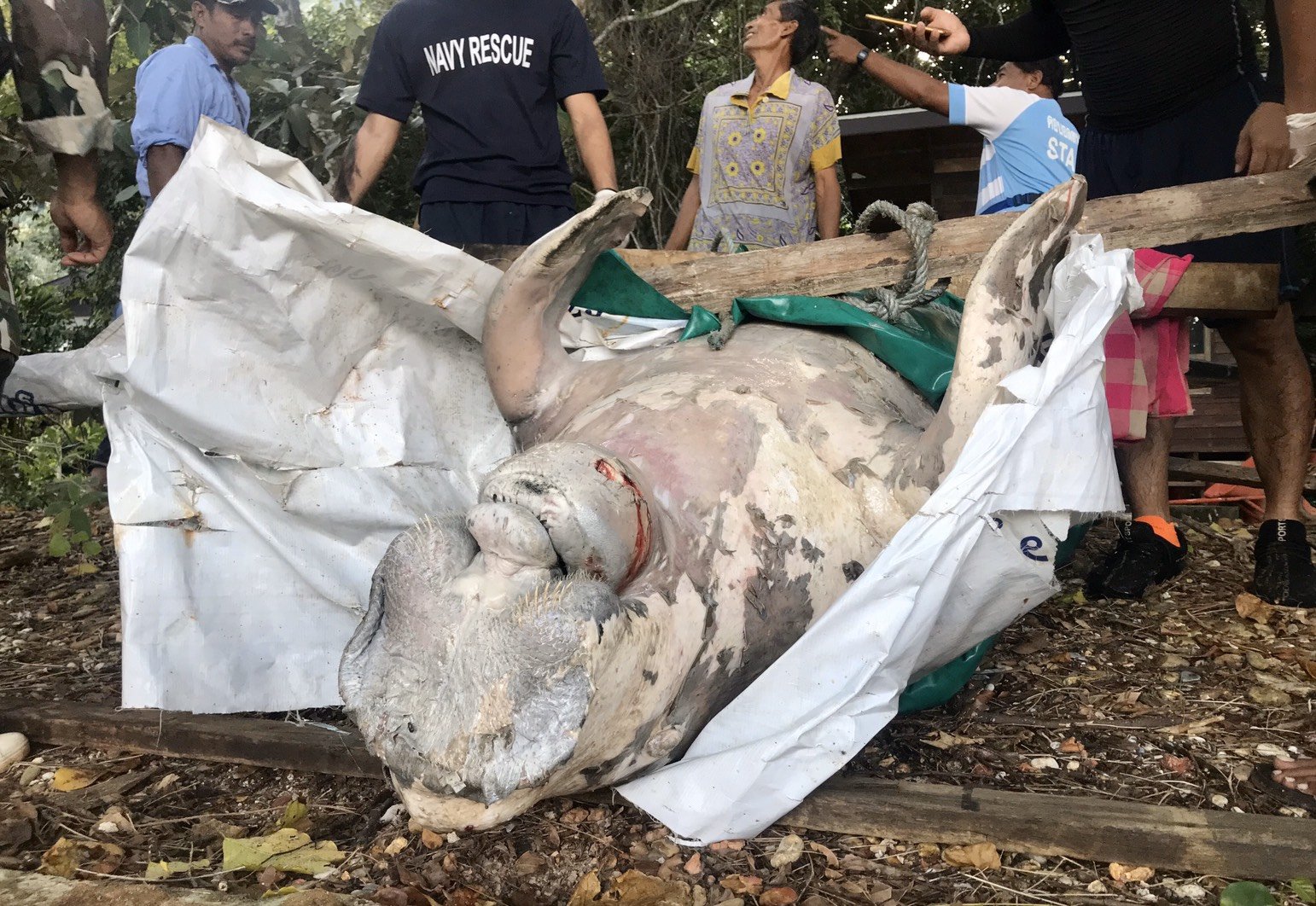
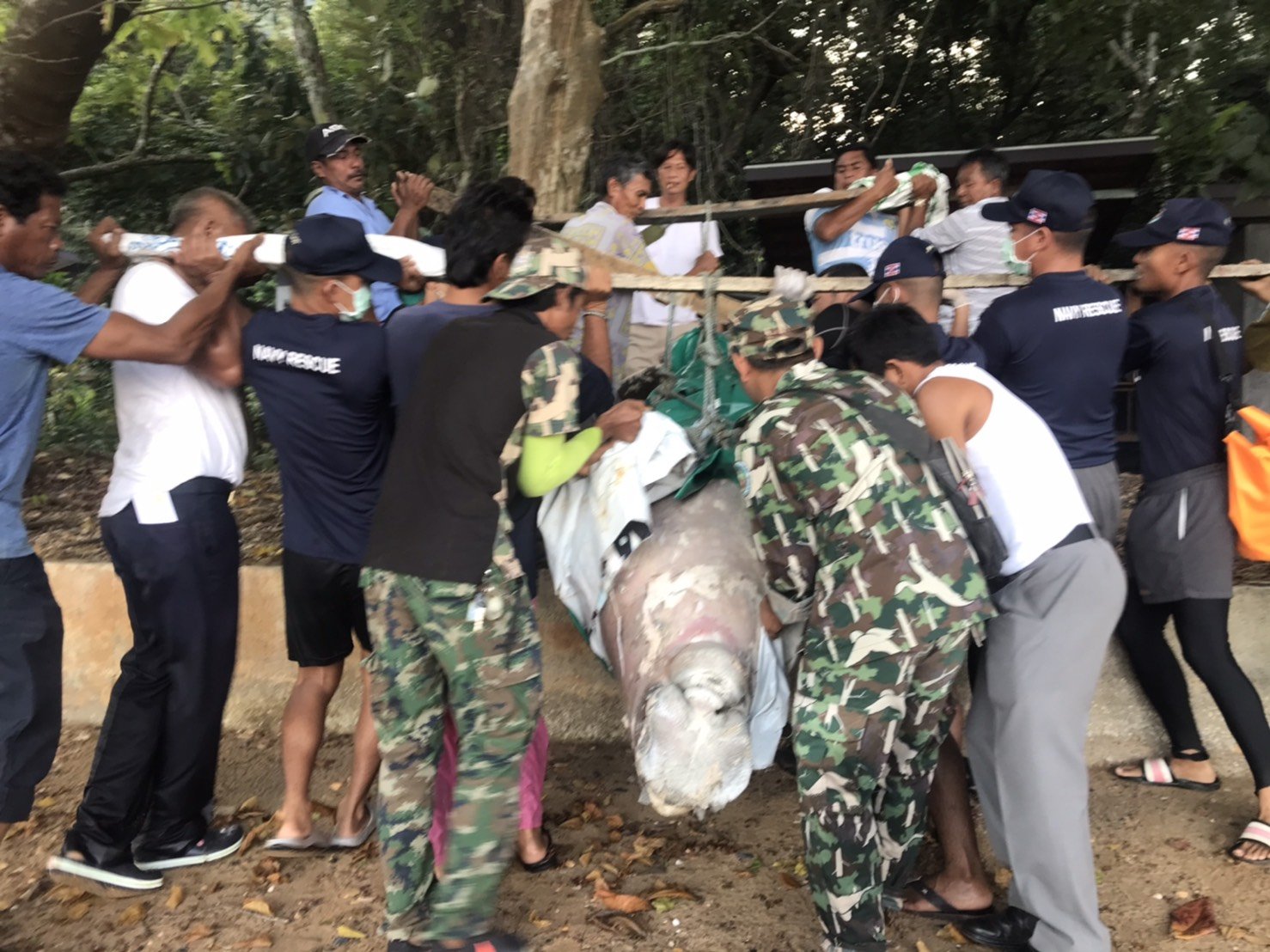
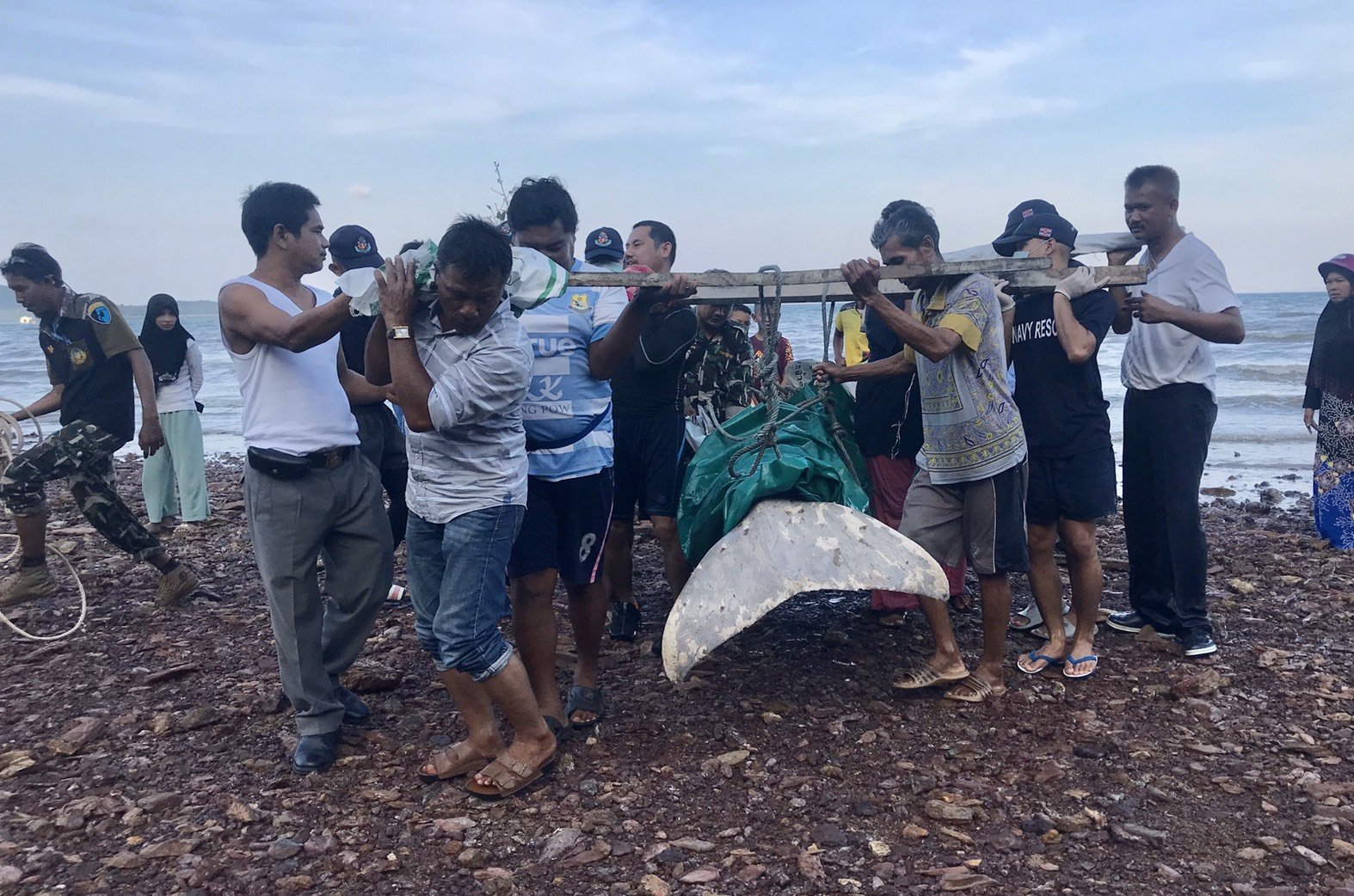
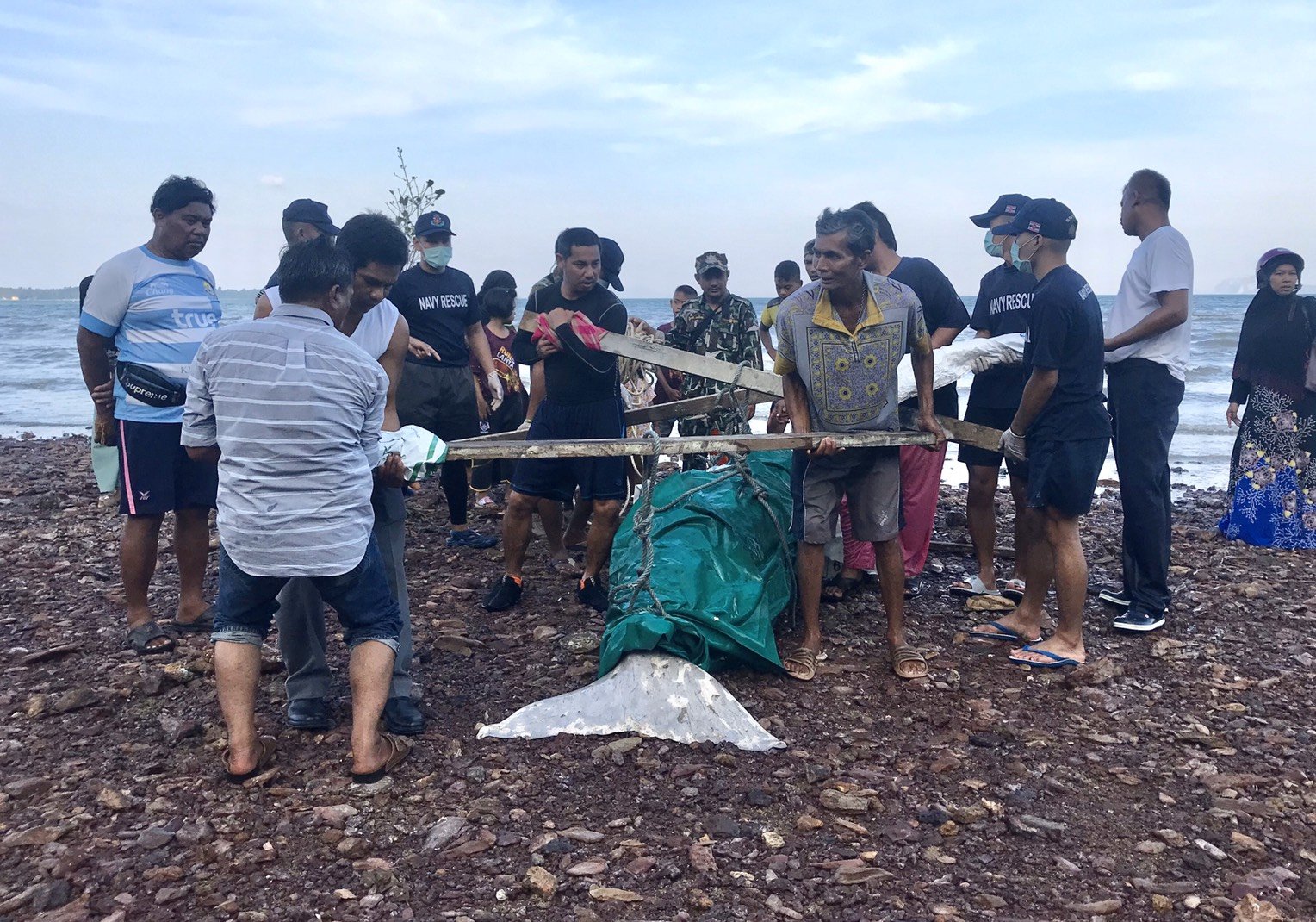
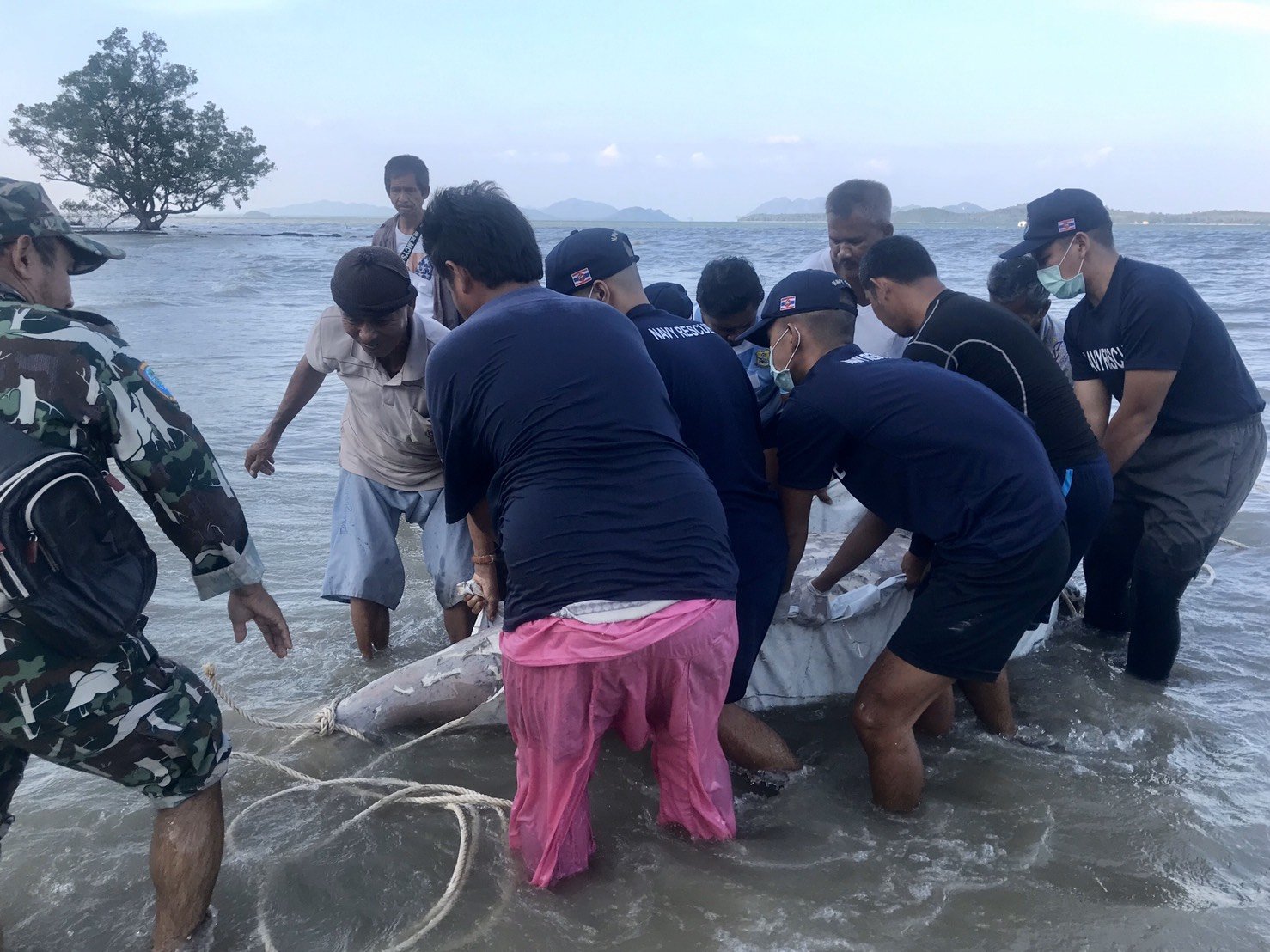
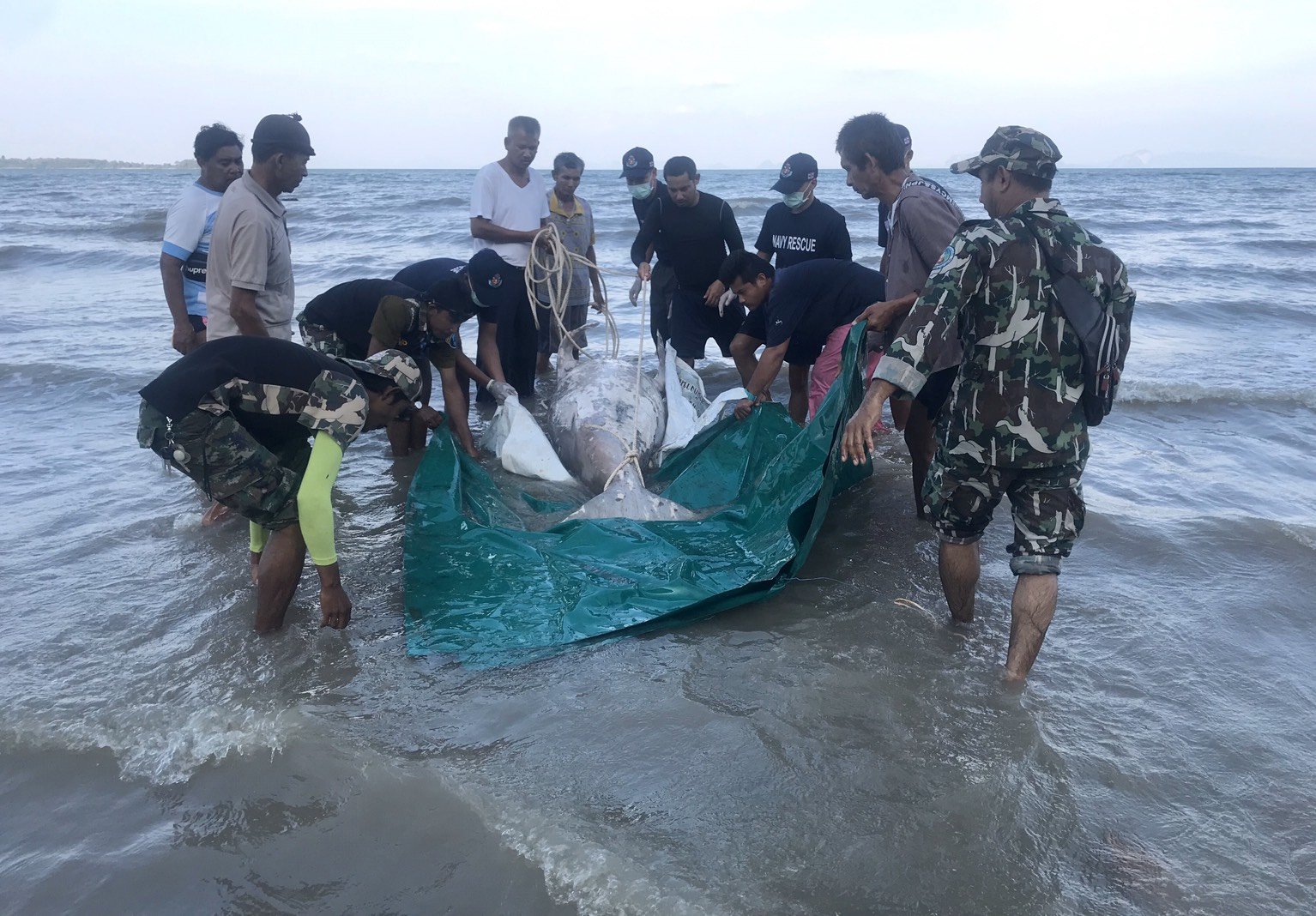
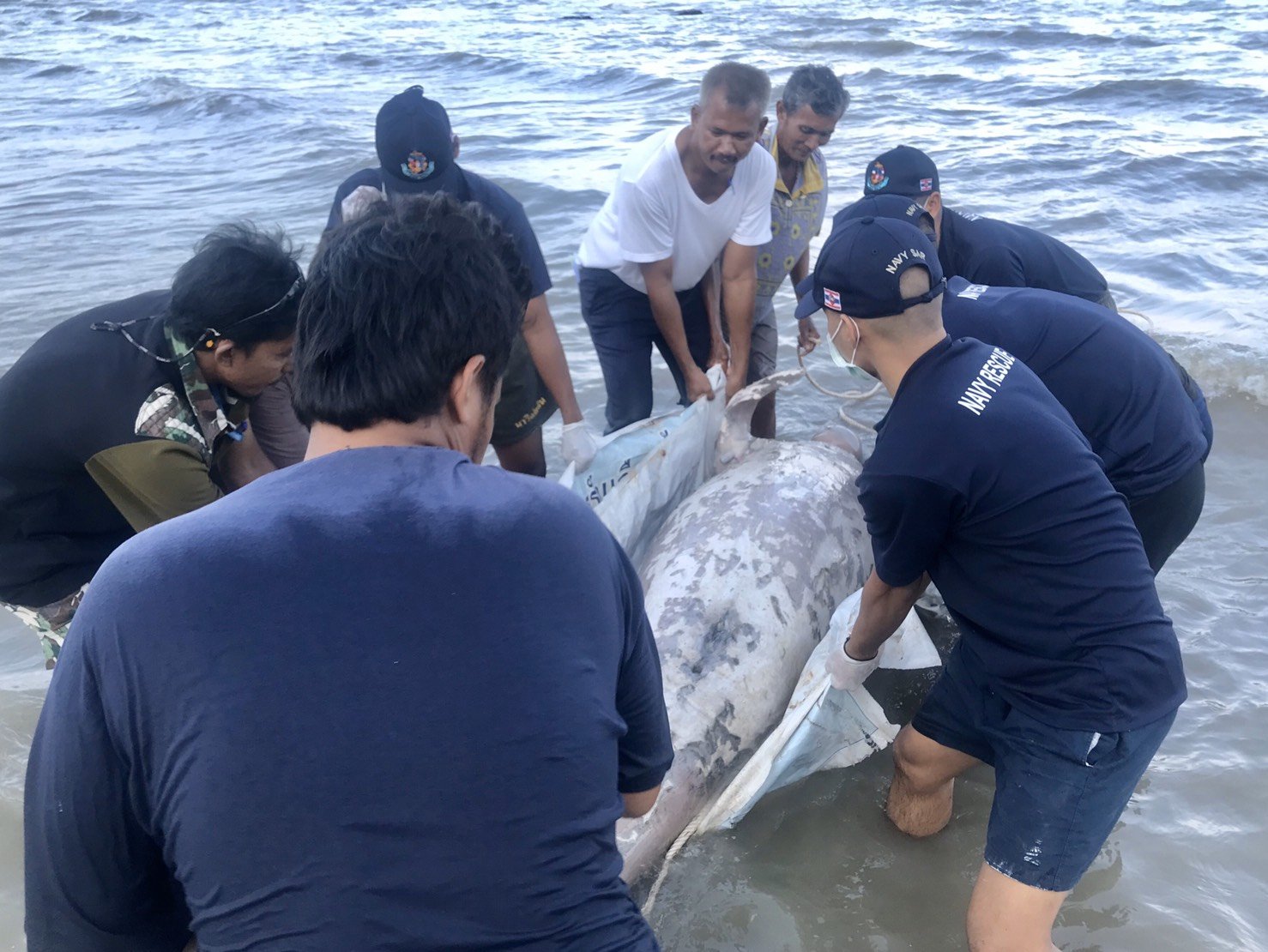
Deceased Dugong Bull found on our beach in Koh Lanta, Krabi Thailand. Plastics were most likely the reason for its death.


















