Hippos
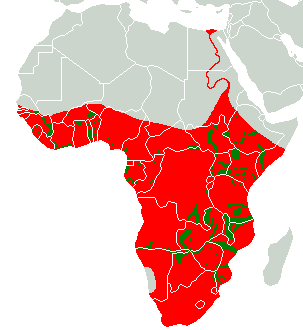
Hippo distribution. Red is historical range and green is current.
The Hippopotamus ( pl: hippopotamuses or hippopotami; Hippopotamus amphibius), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant species in the family Hippopotamidae, the other being the pygmy hippopotamus (Choeropsis liberiensis or Hexaprotodon liberiensis). Its name comes from the ancient Greek for "river horse" (ἱπποπόταμος).
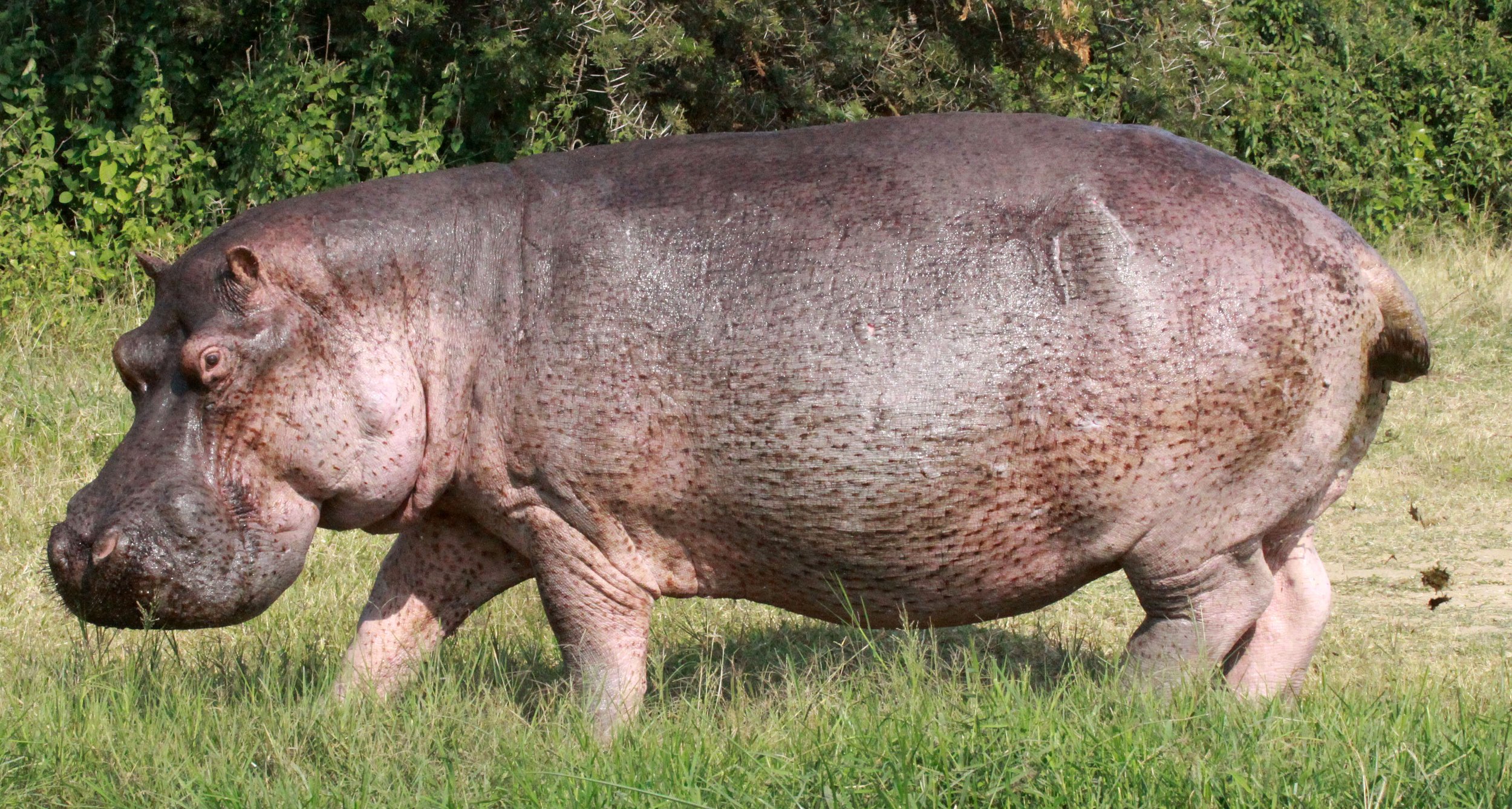
Aside from elephants and rhinos, the hippopotamus is the largest land mammal. It is also the largest extant land artiodactyl. Despite their physical resemblance to pigs and other terrestrial even-toed ungulates, the closest living relatives of the hippopotamids are cetaceans (whales, dolphins, porpoises, etc.), from which they diverged about 55 million years ago. Hippos are recognisable for their barrel-shaped torsos, wide-opening mouths with large canine tusks, nearly hairless bodies, pillar-like legs, and large size: adults average 1,500 kg (3,310 lb) for bulls (males) and 1,300 kg (2,870 lb) for cows (females). Despite its stocky shape and short legs, it is capable of running 30 km/h (19 mph) over short distances.
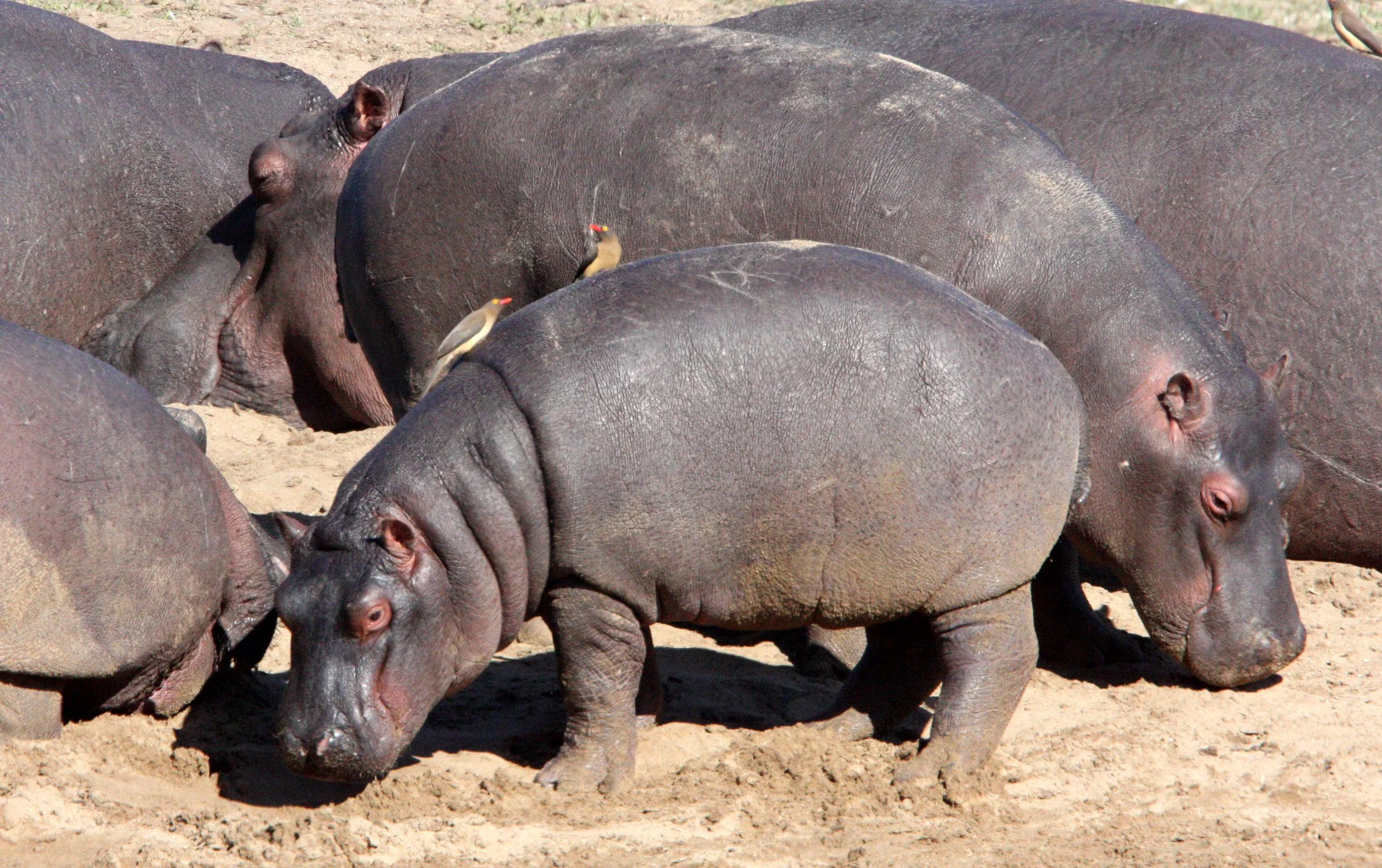
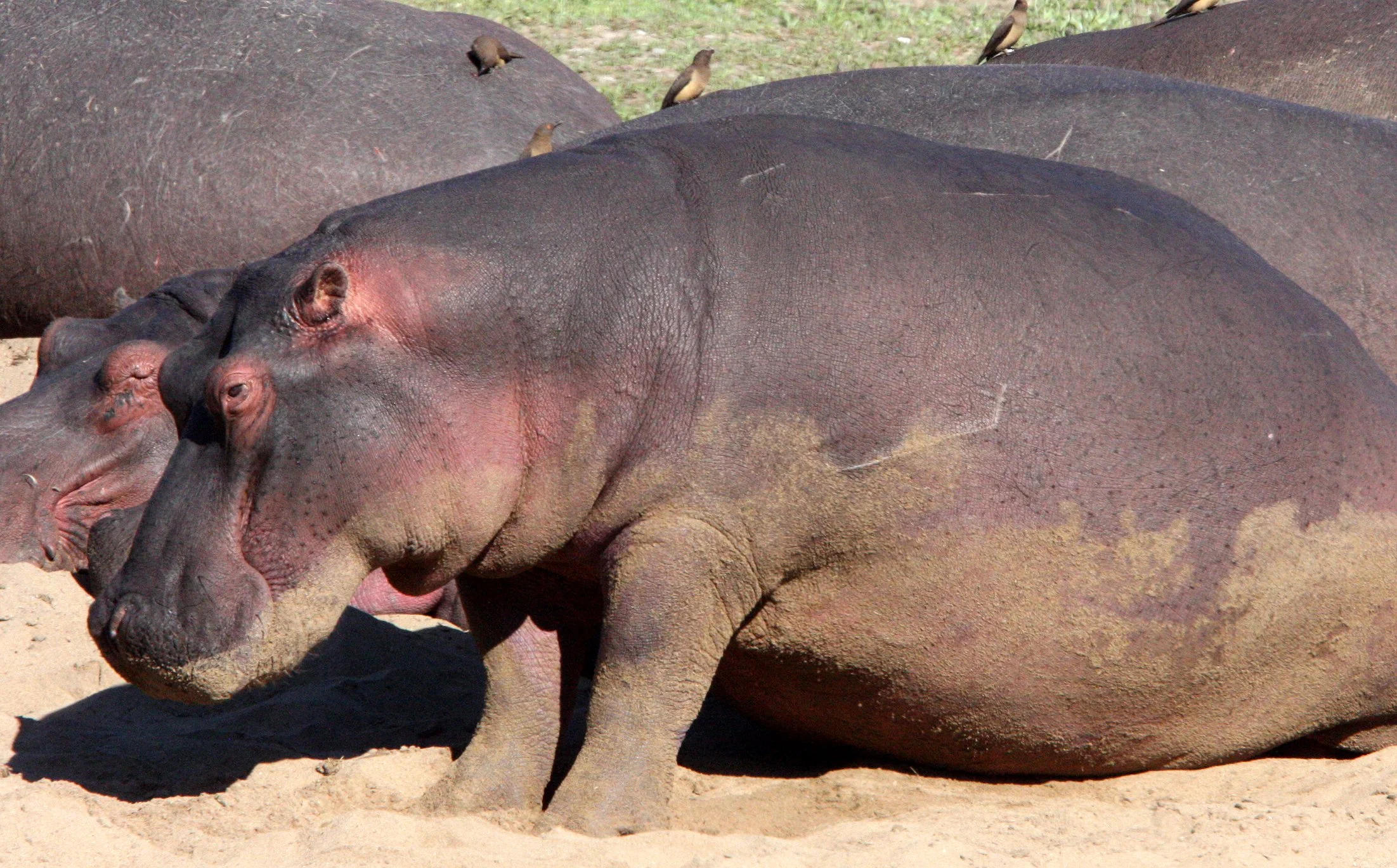
Hippos inhabit rivers, lakes, and mangrove swamps. Territorial bulls each preside over a stretch of water and a group of five to thirty cows and calves. Mating and birth both occur in the water. During the day, hippos remain cool by staying in water or mud, emerging at dusk to graze on grasses. While hippos rest near each other in the water, grazing is a solitary activity and hippos typically do not display territorial behaviour on land. Hippos are among the most dangerous animals in the world due to their aggressive and unpredictable nature. They are threatened by habitat loss and poaching for their meat and ivory (canine teeth).
The modern hippopotamus and the pygmy hippopotamus are the only living members of the family Hippopotamidae. Some taxonomists group hippos and anthracotheres in the superfamily Anthracotheroidea. Hippopotamidae are classified along with other even-toed ungulates in the order Artiodactyla.
Five subspecies of hippos have been described based on morphological differences in their skulls as well as differences in geographical range:
Great northern hippopotamus or Nile hippopotamus H. a. amphibius – (the nominate subspecies) which ranged from Egypt, where they are now extinct, south up the Nile River to Tanzania and Mozambique
East African hippopotamus H. a. kiboko – was present in Kenya in the African Great Lakes region, and in Somalia in the Horn of Africa. Featured broader nasals and a more hollowed interorbital region
Cape hippopotamus or South African hippopotamus H. a. capensis – ranged from Zambia to South Africa; had the most flattened skull of the various subspecies
West African hippopotamus or Tchad hippopotamus H. a. tschadensis – ranged throughout Western Africa to Chad, as the name suggests; featured a slightly shorter and wider face, with prominent orbits
Angola hippopotamus H. a. constrictus – ranged from the southern Democratic Republic of Congo to Angola and Namibia; named for its deeper preorbital constriction